In the paper, we take 6794 English news articles published by national and local press organizations (e.g., Forbes, The New York Times, Newsweek, The Detroit News) between 1975 to 2021 using the keywords “Detroit”, “shrink” and “decline.” These keywords were selected based on the characteristics of the study area (i.e., Detroit) and the phenomenon of urban shrinkage. With these data we then use BERTopic to detect and classify all collected news articles into certain topics. We chose BERTopic because it captures the semantic relationship among words converting sentences and words to embedding and automatically generates the topic unlike other NLP topic modeling techniques (e.g., LDA). Our topic modeling results identify several insights with respect to Detroit's shrinkage. For example, we can detect the side effects of the 2007-2009 economic recession on Detroit's automobile industry, local employment status, and the housing market. If sounds of interest and you want to find out more, below we provide the abstract, some figures from the paper including the methodology workflow and an example of the resulting topics over time. Finally, at the bottom of the page you can see the full reference and s link to the paper itself.
Abstract
Today we are awash with data, especially when it comes to studying cities from a diverse data ecosystem ranging from demographic to remotely sensed imagery and social media. This has led to the growth of urban analytics providing new ways to conduct quantitative research within cities. One area that has seen significant growth is using natural language processing techniques on text data from social media to explore various issues relating to urban morphology. However, we would argue that social media only provides limited insights when dealing with longer-term urban phenomena, such as the growth and shrinkage of cities. This relates to the fact that social media is a relatively recent phenomenon compared to longer-term urban problems that take decades to emerge. Concerning longer-term coverage, newspapers, which are increasingly becoming digitized, provide the possibility to overcome the limitations of social media and provide insights over a timeframe that social media does not. To demonstrate the utility of newspapers for urban analytics and to study longer-term urban issues, we utilize an advanced topic modeling technique (i.e., BERTopic) on a large number of newspaper articles from 1975 to 2021 to explore urban shrinkage in Detroit. Our topic modeling results reveal insights related to how Detroit shrinks. For example, side effects of 2007 to 2009 economic recessions on Detroit’s automobile industry, local employment status, and the housing market.
Key Words: Natural Language Processing, Topic Modeling, Newspapers, Urban Shrinkage, Urban Analytics.
 |
| Vacancy status change from 1970 to 2010 for city of Detroit and surrounding area. |
 |
| Topic modeling work flow. |
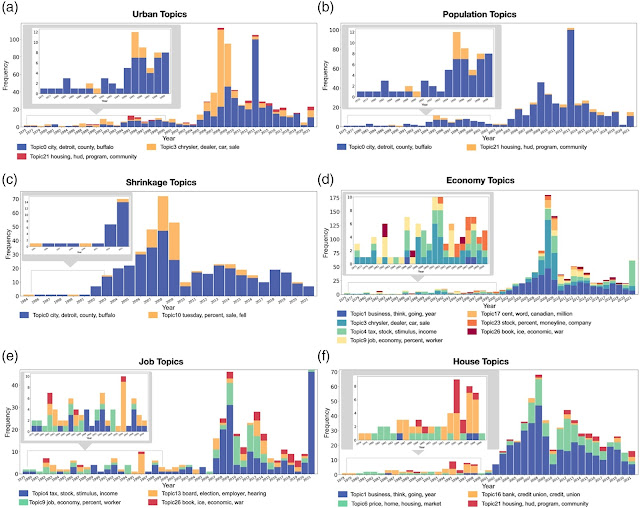 |
| Topics over time (a) urban, (b) population, (c) shrinkage, (d) economy, (e) job, (f) house. |
Full Reference:
Jiang, N., Crooks, A.T., Kavak, H. and Wang, W. (2023), Leveraging Newspapers to Understand Urban Issues: A Longitudinal Analysis of Urban Shrinkage in Detroit, Environment and Planning B. Available at https://doi.org/10.1177/23998083231204695. (pdf)


No comments:
Post a Comment